Introduction
Compared to conventional sex identification methods for birds, such as cloaca inspection, laparoscopy, steroid analysis, and karyotyping, PCR-based sex identification methods are more accurate, sensitive, and less invasive, making them a valuable tool for culling non-target sex, reducing management costs, and promoting the industrialization of pigeon breeding.
The chromosome helicase DNA-binding protein (CHD) gene, which is carried on sex chromosomes in birds, is highly conserved and evolves slowly. In non-columbiform birds such as pigeons and chickens, the CHD gene has one copy on each of the Z and W chromosomes. The exon sequences and sizes of the two chromosomes are similar, but the intron lengths differ significantly. Therefore, it is possible to design specific primers targeting the conserved regions of the gene on either side of the introns to establish a molecular biological method for sex identification in non-columbiform birds.
The preparation:
A total of 36 pigeon feather samples were collected, including 6 samples of known-sex adult pigeons and 30 samples of unknown-sex squabs. Feathers were collected from the wings and tails, typically 3 to 5 feathers per bird. The fluff at the top of the feathers was trimmed with a sterile pair of scissors, and the feather roots with follicles were placed in a 5-mL centrifuge tube and stored at -20°C until use.
Materials for the experiment:
DNA Extraction Kit:
This kit contains all the necessary reagents and equipment to extract DNA from biological samples.
RNase-free ddH2O:
This water is free of RNAase, which is an enzyme that can degrade RNA. It is important to use RNase-free water when working with DNA to prevent contamination.
dNTPs:
These are the building blocks of DNA. They are used to synthesize DNA during PCR.
DEPC:
This chemical is used to decontaminate equipment and reagents to prevent contamination.
2×Taq PCR MIX:
This is a ready-to-use mixture of reagents that are used to amplify DNA during PCR.
DNA Marker DL2000:
This is a standard DNA marker that is used to determine the size of amplified DNA fragments.
Agarose:
This is a polysaccharide that is used to create a gel for separating DNA fragments by size.
PCR Primer Design and Synthesis
The upstream primer F is 5′-GTTACTGATTCGTCTACGAGA-3′, and the downstream primer R is 5′-ATTGAAATGATCAGTGCTTG-3′.
Pigeon Feather Genome DNA Extraction and Quantification
Pigeon feather samples are first washed with 70% ethanol, rinsed with distilled water, and dried. Then, the feather roots with follicles are cut and ground. After grinding, the feathers are transferred to a sterile centrifuge tube with an appropriate amount of sterile deionized water and the supernatant is centrifuged. The pigeon genome DNA is extracted according to the instructions of the DNA extraction kit. The DNA concentration is determined using a microspectrophotometer. The OD260/OD280 ratio is recorded. The samples with better DNA purity are used for PCR amplification.
PCR Reaction
The PCR reaction mixture is 25 microliters: 1.5 microliters of DNA template, 1 microliter each of upstream and downstream primers, 12.5 microliters of Mix, and 9 microliters of sterile deionized water.
The PCR reaction conditions are as follows:
Pre-denaturation at 94℃ for 5 minutes.
35 cycles of denaturation at 94℃ for 30 seconds, annealing at 52℃ for 45 seconds, and extension at 72℃ for 45 seconds.
Extension at 72℃ for 8 minutes.
The PCR products are detected by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Results:
Females have two bands (at 660bp and 450bp).
Males have only one band, approximately 660bp.
DNA was extracted from the feathers of pigeons, rabbits, sheep, and pigs, respectively. The PCR was performed according to the above method to test the specificity of the method.
The results of the PCR reaction are as follows:
Pigeon feathers: Two bands, 660bp and 450bp, were observed.
Rabbit fur: No bands were observed.
Sheep wool: No bands were observed.
Pig hair: No bands were observed.
These results indicate that the PCR method is specific for the CHD gene. The CHD gene is present in the sex chromosomes of birds, but it is not present in the sex chromosomes of other animals. Therefore, the PCR reaction will only amplify the CHD gene from DNA extracted from bird feathers.
The results of this experiment are consistent with the expected results. The CHD gene is a highly conserved gene that is present on sex chromosomes in birds. The primers used in this experiment are designed to be specific for the CHD gene. Therefore, the PCR reaction is only expected to amplify the CHD gene from DNA extracted from bird feathers.
Pigeon Genome Extraction Results
The nucleic acid test results showed that the purity of the pigeon genome DNA was high (OD260/OD280 results were between 1.8 and 2.0), which could be used for subsequent PCR reactions.
PCR Amplification Results of Pigeons with Known Sex
The target fragments amplified by PCR were consistent with the expected size, as shown in Figure 1.
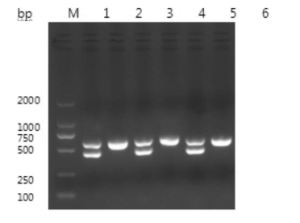
The sequence of the CHD-Z gene with a fragment size of 656 bp was obtained by sequencing. The comparison analysis results showed that the homology of the CHD-Z gene sequence of the pigeon sequenced this time was 99.2% with the known sequence. The sequence of the CHD-W gene with a fragment size of 448 bp was obtained by sequencing. The comparison analysis results showed that the homology of the CHD-W gene sequence of the pigeon sequenced this time was 99.8% with the known sequence.
PCR Specificity Test Results
The specificity test results showed that the DNA samples extracted from the feathers of pigeons with known sex can all amplify the target bands that are consistent with the expected size. However, the samples of rabbit fur, sheep wool, and pig hair did not amplify the target bands, indicating that the method is specific for the CHD gene.
These results are consistent with the expected results. The CHD gene is a highly conserved gene that is present on sex chromosomes in birds. The primers used in this experiment are designed to be specific for the CHD gene. Therefore, the PCR reaction is only expected to amplify the CHD gene from DNA extracted from bird feathers.
PCR specific results
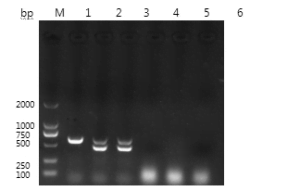
Samples; 4 is a rex rabbit hair sample; 5 is a sheep wool sample; 6 is a pig hair sample.
The following are some additional details about the results:
The OD260/OD280 ratio is a measure of the purity of DNA. A ratio of 1.8 to 2.0 indicates that the DNA is highly pure.
The PCR results showed that the target fragments were amplified to the expected size. This indicates that the primers were designed correctly and that the PCR reaction was performed correctly.
The sequencing results showed that the amplified fragments were identical to the known sequences of the CHD-Z and CHD-W genes. This confirms that the PCR reaction was specific for the CHD gene.
The specificity test results showed that the PCR reaction only amplified the CHD gene from DNA extracted from bird feathers. This indicates that the method is specific for the CHD gene and can be used to determine the sex of pigeons.