Specifica: 4*50ML
| Reagente | Composition |
|---|---|
| Reagente (UN) | Crystal Violet Staining Solution |
| Reagente (B) | Acidic Ethanol Differentiation Solution |
| Reagente (C) | Ammonium Oxalate Crystal Violet Staining Solution |
| Reagente (D) | Weigert’s Iodine Solution |
Magazzinaggio: Temperatura ambiente, avoid light
Descrizione del prodotto:
- Gram Staining:
- Invention:
- Invented by Danish physician Christian Gram in 1884.
- Method:
- Widely used differential staining method in bacteriology.
- Form of counterstaining.
- Purpose:
- Differentiates bacteria into two major classes:
- Gram-positive (G*)
- Gram-negative (G)
- Differentiates bacteria into two major classes:
- Mechanism:
- Differential staining based on differences in:
- Permeability of cell wall to ethanol
- Ability to resist decolorization
- Thickness and structure of peptidoglycan layer
- Differential staining based on differences in:
- Staining Process:
- Cells stained with crystal violet and then treated with iodine form insoluble complexes.
- Decolorized by ethanol.
- Isoelectric Points:
- Gram-positive bacteria: isoelectric points at pH 2.0-3.0
- Gram-negative bacteria: isoelectric points at pH 4.0-5.0
- Binding Properties:
- Gram-positive bacteria carry more negative charges.
- Bind more tightly to basic dyes such as crystal violet.
- Formation of Complex:
- After addition of mordant (iodine) into bacterial cells:
- Crystal violet-iodine-protein complex insoluble in water is formed.
- Binds to ribonucleic acid magnesium salts inside Gram-positive bacteria.
- After addition of mordant (iodine) into bacterial cells:
- Risultato:
- Stained bacteria less prone to decolorization.
- Invention:
Operating Steps (for reference only):
- Tissue fixation in 10% formalin, routine dehydration embedding.
- Cut sections to a thickness of 4μm, and dewax routinely to water.
- Drop staining slices in crystal violet staining solution for 5 minuti, then discard the dye.
- Differentiate in acidic ethanol differentiation solution for 2-5 secondi.
- Rinse with flowing water for 3-5 secondi.
- Drop staining slices in ammonium oxalate crystal violet staining solution for 5 minuti, then discard the dye. Use paper to gently absorb excess liquid around the slices.
- Treat slices with Weigert’s iodine solution for 1 minuto, then discard the iodine solution. Repeatedly absorb the moisture inside the slices with filter paper.
- Differentiate with the ortho-toluidine-xylene solution until there is no purple color leaching out of the slices. Immediately wash with xylene, and observe under a microscope. Repeat washing with fresh xylene several times to thoroughly remove orthotoluidine. Seal with neutral resin.
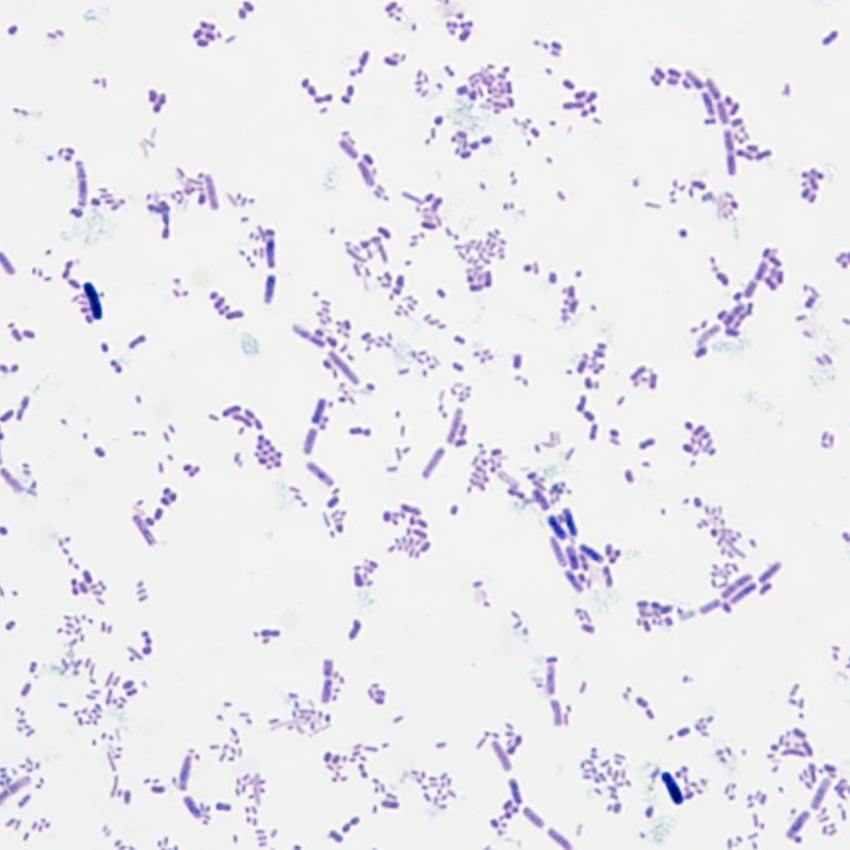
Staining Results:
- Gram-positive bacteria and cellulose: Blue-purple
- Gram-negative bacteria: Red
- Cell nucleus: Red
Customers’ Reviews Of Solarbio Products For Reference



Recensioni
Non ci sono ancora recensioni.